Early ripe sweet variety of honeysuckle Leningrad giant
Russian gardeners grow more than 70 varieties of honeysuckle. One of the most beloved is the Leningrad giant. Due to its resistance to adverse factors, blue honeysuckle is suitable for cultivation in the northern and eastern regions.
The content of the article
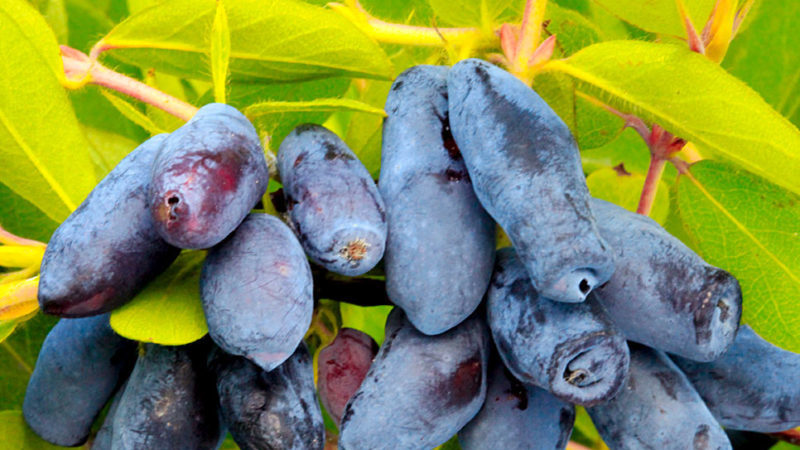
Description of the variety of honeysuckle Leningrad giant
It is an early maturing variety with very sweet fruits. He became a good donor for breeding new hybrids. Differs in the ability to form berries in bunches that do not crumble.

Origin and development
The variety was developed at the Pavlovskaya station named after N.I. Vavilov in St. Petersburg under the leadership of M.N. Plekhanova. Obtained by the seed method from the wild Kamchatka honeysuckle.
Characteristics, description of appearance, taste
It is a vigorous shrub up to 1.5-2 m high. After the end of the fruiting period, the bark acquires a brown hue and cracks, peeling off in long strips.
Some more features of the variety:
- leaves are dark green, oval, large, slightly elongated, 5 cm long, about 3 cm wide;
- flowers are pale yellow, bell-shaped;
- berries are dark blue, have the shape of an elongated cylinder with a rounded base.
The variety is self-fertile, blooms, but does not form ovaries. Needs additional pollinators in the form of edible honeysuckle Blue spindle, Morena, Bluebird.
Honeysuckle is characterized by high taste. The berries have a thin but dense skin with a light waxy coating. The pulp is tender, sweet and sour, aromatic. The bitterness is completely absent. Tasting score - 4.8 points.
Application features
it edible variety. Berries are consumed fresh, used to make jam, jam, compote.
Productivity and fruiting
The yield of an adult bush is from 3 to 5 kg. With proper care and adherence to the watering regime, the bush is guaranteed to give about 3 kg of berries. Fruit length - about 3 cm, thickness - about 2 cm, weight - from 1.2 to 4 g.
Long-term fruiting. It starts in July and ends in August.
Ripening period
Ripening period is early, late June - early July.
Disease and pest resistance
Often, honeysuckle is affected by powdery mildew, the rhesus mosaic virus. The main types of pests are honeysuckle mites, scale insects, aphids, leafworm caterpillar.
Cold and drought resistant
The Leningrad giant has good frost resistance. Roots and shoots do not freeze at -40 ° C, flowers and ovaries during the growing season do not lose their viability at -8 ° C. The bush is undemanding to heat, but in dry summers it requires regular watering.
Growing regions and climate requirements
It grows well in the middle lane and in the north-west of Russia. It develops well at low temperatures from -8 ° С and above without loss of properties.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
Advantages:
- massive berries;
- there is no bitterness;
- shedding of overripe fruits is excluded;
- convenient to pick berries;
- high yield rates;
- stable fruiting;
- there is no tendency to re-bloom;
- excellent frost resistance;
- early maturity of the bush - berries appear already for 3 years.
Disadvantages:
- requires pollinators;
- needs regular shrub formation.
Difference from other varieties and hybrids
Distinctive features - large fruits weighing up to 5 g, pleasant taste without bitterness, no discharge of overripe fruits, early maturity.
Agrotechnics
Cultivation of culture implies choosing the right time and place of landing. Also, we must not forget about further care, which will affect the quality of the crop.
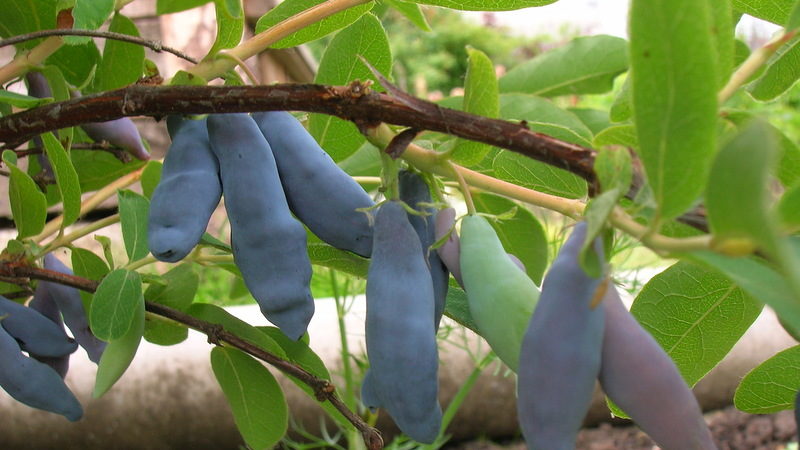

Choosing a place in the garden and preparing holes
Planting work plan from late July or early August to November. Choose an open area with lots of sunlight. Do not plant honeysuckle in damp and low-lying areas, as the roots will be washed by groundwater. Excessive moisture will lead to the death of the shrub.
During planting operations, the moisture content of the soil and air must be at least 85%. Air temperature - + 20 ... + 25 ° С, soil - + 15 ... + 17 ° С.
Wells are prepared according to the following principle:
- Leave a distance between them from 2.5 to 3 m.
- Dig holes 50x50 cm in size.
- Drainage from crushed brick or expanded clay is poured to the bottom.
- Next, fill with earth, consisting of 20 liters of humus, 30 g of superphosphate and 30 g of potassium salt or 500 g of ash.
2 hours before planting the bushes, the holes are watered abundantly. Then they wait until the moisture is absorbed, and start planting the plants.
Preparing for landing
Experienced gardeners recommend purchasing honeysuckle seedlings at the age of 3 years. Their height should be up to 40 cm. The presence of 2-3 flexible branches with live buds is mandatory. There should be no rot on the root system.
2 hours before planting, the roots of the plants are immersed in water. Add growth stimulants "Kornevin" or "Heteroauxin" strictly according to the instructions.
Ground requirements
Optimal soil option - nutritious sandy loam mixture with neutral acidity (up to 5-7 pH). The condition of the soil is improved by adding 1.5 kg of dry vermicompost. The earth is dug up and watered abundantly.
Timing, scheme and landing rules
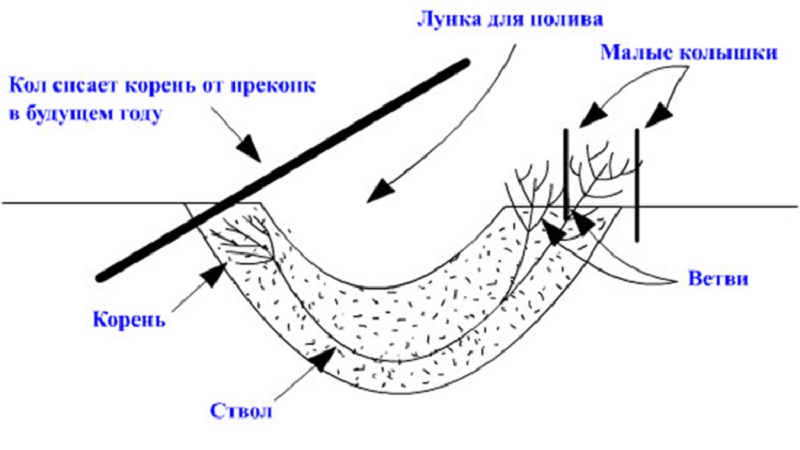
The best time to plant is from August to November. The dimensions of the holes are 50x50x50 cm, the distance between them is 2.5-3 m.
Step-by-step instruction:
- After absorbing moisture, the hole is filled to the top with earth.
- Place the plant, gently straighten the roots.
- They compact the soil well.
- The root collar is buried 5 cm in the ground.
- Grooves are formed around the bush, 10 liters of water are poured into them.
- Straw or hay is laid out under the plant in a layer of 10 cm.
Landing ahead of schedule negatively affects honeysuckle. Vegetation begins at the end of March. During this period, the plant devotes all its strength to the formation and blooming of buds and is not able to adapt to a new place.
Growing features
The Leningrad giant needs proper care. The bushes are regularly examined for the presence of diseases and pests, and are formed. Experienced gardeners recommend alternating honeysuckle with dogwood, barberry, black currant, pollinating varieties.
Honeysuckle requires regular watering, loosening the soil and top dressing. An important nuance when growing it is pruning. Crown formation begins in the third season. Only 5 strong branches are left, the root shoots and non-fruiting small branches are completely cut out.
Thinning is carried out in the fall, after the foliage has completely fallen off, at a temperature of about -3 ° C. Do not cut off the top of the shoots, as flower buds are formed there.
Watering recommendations:
- for the entire season, honeysuckle requires 7 waterings, during the dry season - 14;
- one bush requires up to 15 liters of water;
- during the period of fruit filling, the volume of liquid is increased to 30 liters;
- pre-defend water in the sun, bring it into the grooves made;
- watering bushes with a hose, irrigating leaves and branches to increase moisture;
- then loosen the soil, lay a layer of mulch of dry leaves or straw to prevent moisture from evaporating from the soil.
Honeysuckle must be fed:
- Fertilizers are applied in the spring, starting from the third season.
- Recipe for nitrogen fertilizing: 2 tbsp. l. urea is dissolved in 10 liters of water, 2 liters are added under each bush.
- After the snow melts, mineral fertilizing is applied in the form of 10 kg of humus. Gently dig up the soil around the plant.
- In the phase of formation of buds and ovaries, they are watered with an ash solution. Recipe: 1 liter of ash is dissolved in 10 liters of water, 2 liters are added under each plant.
- In autumn, 5 kg of compost, 100 g of ash, 40 g of superphosphate per 1 square meter are introduced into the groove. m. Every 2 years, potassium salt is added to this mixture in an amount of 15 g per 1 sq. m.
Pollinators
The best pollinators for the Leningrad giant are honeysuckle varieties Blue Spindle, Morena, Blue Bird.
Disease and pest control
The variety is affected by powdery mildew. The fungus attacks the plant in drought. Leaves and shoots are covered with whitish spots. Prevention is regular watering, planting shrubs only in a well-lit place. Plants are treated with Skor, Vectra preparations strictly according to the instructions.
When damaged by a mosaic, the leaves are covered with reddish dots. They gradually turn yellow and fade. Preventions include weed control, moderate watering. Plants are treated with "HOM", "Ditan M-45" strictly according to the instructions.
Pests:
- Aphid. The berry is placed only in a sunny area, the planting is not thickened, mint, tansy, and chamomile are planted next to it. If there are ants on the site, they are treated with the "Anteater". Also use "Nitrafen", "Kilzar" according to the instructions.
- Honeysuckle mite. Signs are wrinkling of leaves and fruits. Prevention involves thinning the crown of the bush. The fight includes spraying with "Decis", "Inta-Vir" according to the instructions.
- Leaf roll. Signs are twisted, eaten leaves. For prevention, the soil is loosened, the berries are harvested by hand. Wrestling - spraying with "Decis", "Aktara", "Biotlin" according to the instructions.
- Shield. Signs - growths on the bark, the berry dries up and dies. The fight includes burning of diseased branches, spraying with "Rogor" and "Aktellik" according to the instructions.
Preparing for winter
Honeysuckle requires no cover. But on the eve of a cold snap, it is poured with 30 liters of water, and a layer of compost is laid on the soil.
Reproduction

Produced in three ways:
- By division. The bush at the age of 5 at the end of summer is divided into parts with roots and 3 branches. New plants are planted in separate holes. The preparatory work is described above.
- Layers. In June, the top of the shoot is pinned to the ground, sprinkled with a layer of 5 cm and watered. Separate it from the mother plant for next year in the fall. Use the planting rules above.
- By cuttings. The instruction is as follows:
- at the end of autumn, lignified annual growths are cut into pieces of 20 cm;
- they are placed in a box with sand or sawdust and sent to the basement until spring;
- after the snow melts, cuttings are planted in the greenhouse at an angle of 45 °;
- planted in open ground in the fall according to the above rules.
Cutting differs from other methods in the high survival rate of plants.
Growing difficulties
When growing honeysuckle, the Leningrad giant does not have any difficulties. Even beginners do a great job with this process.
Harvesting
The timing of harvesting fruits depends on the growing region. But experienced gardeners advise using the rule: berry picking begins when birds appear in the garden, otherwise they will destroy the entire crop.
How and when to collect
In central Russia, honeysuckle begins to be harvested in mid-July. The fruiting period stretches until August, so the shrubs are regularly inspected for the presence of ripe berries. The fruits are collected in bunches. They are torn off, placed in a refrigerator, or eaten immediately.
Advice and feedback from experienced gardeners

Recommendations:
- plant only bushes at the age of 3 years;
- choose a well-lit area for planting;
- observe the irrigation regime, the timing of top dressing;
- inspect the berry for diseases and pests;
- do not forget about mulching the soil.
Gardeners speak positively of the Leningrad giant.
Elvira, Sochi: “Honeysuckle The Leningrad giant grows well, the berries are very large. Their taste is much better than that of the Bakcharsky giant variety. There are a lot of bumblebees. But it is not always possible to harvest because of the birds. "
Irina, Tomsk: “Honeysuckle Leningrad giant has been growing since 2014, but still has not lost the quality of fruiting. The berries are large, tasty, and go well with homemade yogurt. I recommend mulching the soil around the bush in hot summer. "
Conclusion
The Leningrad giant honeysuckle variety has proven itself well among Russian gardeners. The plant does not require special care, a special climate for normal development. It is enough to follow the recommendations and advice of experienced gardeners, and then the honeysuckle will delight you with a rich harvest.