Propagating honeysuckle by cuttings - the easiest way!
Edible honeysuckle is unpretentious, frost-hardy, its harvest ripens earlier than other crops - at the end of May or in June. Decorative honeysuckle are shrubs and lianas that are distinguished by exotic beauty and spicy, fruity-vanilla aromas during flowering. In this article we will tell you how to propagate honeysuckle, what are the advantages and disadvantages of each method.
The content of the article
Breeding features of honeysuckle
Honeysuckle reproduces by vegetative means and by seeds. With vegetative propagation, the beginning and end of the growing season of the plant are taken into account, because honeysuckle wakes up when there is still snow, and ends development in July.
The timing depends on the chosen method:
- cuttings are carried out from the beginning of flowering to leaf fall;
- the division of the bush is carried out in early spring or autumn after the leaves fall;
- layering is fixed in the soil in early spring or summer during the growing season;
- seeds - in spring, summer, autumn.
When propagating by cuttings, optimal conditions are created for the formation of a strong root system - a temperature of + 20 ... + 25 ° C and a humidity of 90-95%.
How to choose a parent plant
Vegetative propagation methods are simple and reliable, since they retain 98% varietal characteristics, and the survival rate of seedlings is high.
When choosing a parent plant for obtaining seedlings, they are guided by the rules:
- select a bush of the desired variety;
- choose a strong and healthy plant;
- for dividing the rhizome, a plant is taken at the age of 5-6 years.
Honeysuckle breeding methods
There are several vegetative ways:
- reproduction by layering is suitable for bushes with strong lower annual shoots;
- cuttings are suitable for all types of honeysuckle, cuttings are harvested from spring to autumn;
- root suckers - shoots that have grown from a root accessory bud (rarely formed);
- plant propagation at the age of 5-6 years by dividing the rhizome.
Breeders are mainly engaged in growing from seeds. Reproduction of honeysuckle in this way can lead to the loss of varietal traits in seedlings. This is due to the fact that the plant is cross-pollinated.
Cuttings
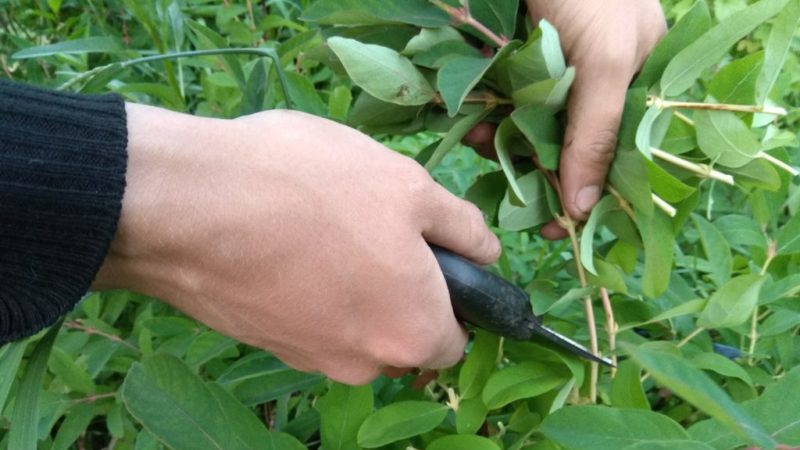

The method consists in harvesting and germinating honeysuckle cuttings. Young green shoots of the current season and annual lignified branches are suitable for this.
How to cut honeysuckle in summer or autumn:
- Choose a fruiting branch 1 year old.
- Cut cuttings 10-12 cm long from it. Cut at an angle of 45 °. Each cutting should have 2-3 internodes with dormant buds.
- Remove the leaves from the bottom and treat it with a stimulant ("Epin", "Kornevin"). Cut the top leaves in half.
- Place the cuttings in water or a nutritious moist substrate (peat + sand) so that the internode is submerged in the substrate or water. Roots are formed on it.
- When the roots are 5-8 cm long, plant the plant in open ground or in a container.
In the first 3 weeks, the cuttings are kept in greenhouse conditions (warm, humid, diffused light) for rapid root germination. To create a greenhouse effect, cut plastic bottles are used.
Read also:
How gooseberries reproduce - all ways
Dividing the bush
 The best time to breed by division is September and October. Before dividing the bush, in spring, the plant is spud to a height of 30 cm to activate the growth of lateral roots.
The best time to breed by division is September and October. Before dividing the bush, in spring, the plant is spud to a height of 30 cm to activate the growth of lateral roots.
Procedure:
- Choose a bush 5-6 years old. In plants over 6 years old, it will be difficult to separate the root ball.
- Dig up the honeysuckle.
- Divide the bush into several parts with a pruner or saw
- Treat the root cut with potassium permanganate or ash.
- Plant the delenki in new places at a distance of 2-2.5 m from each other.
You can carry out a partial division of the bush. For this, 3-4 side branches with roots are separated and planted in a new place.
Attention! Each division should have 3 or more shoots and a developed root.
Horizontal layering
This method is the simplest and least time consuming. Instructions for the procedure:
- In the spring, choose a bush with strong lower annual shoots.
- Weed and loosen the soil under the bush.
- Gently press the branches to the ground and secure with slingshots.
- To stimulate root formation, cut the bark of the pinned branch.
- Pour a 5 cm layer of soil on top.
- Water and keep the ground always moist.
Until autumn, the branch will grow roots, and new shoots will appear. The following spring, the seedlings are separated from the mother plant with pruning shears and transplanted to a new location.
Air layering
This method is used when the branches on the bush are vertical and cannot be bent to the ground.
What to do:
- In the spring, select a branch and make cuts in the bark.
- Wrap the cut bark areas with moss and place in a vertically cut polyethylene bottle with a nutrient substrate.
- Wrap the bottle around a branch, secure it and seal the cut with tape.
- Make sure that the soil in the container is always moist.
- After the roots appear, cut off the branch and plant in the ground for growing.
Root offspring
The formation of root suckers is rare when the roots are overgrowing. In this case, the adventitious root bud wakes up and gives an underground shoot.
This shoot is separated from the mother bush after 2 years and transplanted to a new location.
Seeds
During seed propagation, the varietal properties of the plant are often lost. Cultivated, wild or ornamental honeysuckle can grow from seeds due to cross-pollination. It's hard to predict.
How to plant:
- Crush ripe large berries, distribute on a napkin and dry.
- Plant the dried seeds in the soil to a depth of 0.2 cm and water.
- Cover with foil or glass.
Shoots will appear in 15-20 days.
If the seeds are planted in June, sprouts will appear by the fall, which are covered for the winter so that they will continue to grow in the spring. You can plant seeds before winter and wait for sprouting in spring. The third way is to plant in prepared soil in March.
After a year, seedlings from seeds are transplanted to a permanent place.
Which is the easiest way and why

According to gardeners, the easiest way is to propagate honeysuckle with horizontal layers. The advantages of this method:
- during growth, the layers are fed from the mother plant;
- the procedure for forming a layering is simple;
- no need to prepare additional soil;
- no need for growing containers and containers.
However, if the honeysuckle bushes have only vertical branches, the easiest way to propagate is by cuttings. With this method, a large number of plants can be planted at the same time.
Terms of the procedure
Reproduction is carried out in spring, summer and autumn, depending on the method:
- reproduction by layering - in early spring and autumn, a month before the onset of frost;
- division of the bush - in September and October, so that the plant has time to adapt in a new place before frost;
- cuttings of the current season are in May and June, the best time is the end of flowering (if you cut them earlier, their viability will be much lower);
- cuttings 1 year old, lignified, cut off after leaf fall or in early spring.
The nuances of breeding edible and decorative honeysuckle

Edible and decorative honeysuckle belong to the same family, so the rules and timing of breeding do not differ:
- 3-4 varieties of honeysuckle are planted on the site for cross-pollination and increasing yields.
- Provide greenhouse conditions for the growth of seedlings (heat, high humidity, a lot of scattered light).
- Cuttings are made no longer than 15 cm, otherwise the root system will be weak.
- Young unhardened plants are not planted in open ground before frost. Do it in the spring or cover it with peat, leaves. It is optimal to plant a two-year-old plant in the ground.
- The soil mixture for planting is prepared light, drained, with a slightly acidic reaction (pH 5.5-6.5). Before planting, 3 kg of compost or rotted manure, 300 g of ash, 3 tbsp. l. "Nitrofoski". Drainage - expanded clay, broken brick.
Conditions for successful breeding
Success in growing edible and ornamental honeysuckle varieties depends on several conditions.
Choosing a landing site
Honeysuckle loves the sun. They plant it in lighted places, protected from the wind. It is optimal if this is the lower part of the slope or elevated places without a close occurrence of groundwater.
Watering
Water the honeysuckle regularly during the dry season, 1-2 buckets per bush. Make sure that the ground under the bush is slightly damp. The plant does not tolerate stagnant water and may die.
Young seedlings and bushes especially need regular watering during the ripening period of berries. A sufficient amount of moisture removes bitterness from the berries.
Top dressing
2 years after planting, the plant will need regular feeding. In the spring, organic matter (rotted manure) is added to the trunk space and poured with a urea solution (1 tbsp. L. Per bucket of water). After fruiting, they are fed with double superphosphate.
Pruning
Edible honeysuckle bushes are pruned 5 years after planting. It is carried out in early spring before bud break or in autumn after leaf fall. Dry old branches are cut out, 6-8 strong shoots are left.
Ornamental types of honeysuckle are subjected to formative pruning as needed at the same time, in order to give the plant a more aesthetic appearance.
Diseases and pests
Sometimes honeysuckle is attacked by fungal infections, especially powdery mildew. This happens if the summer is humid and there are not enough sunny days. The plant is treated with Fitosporin or other fungicides.
Of pests honeysuckle is more often affected by leafworm and aphids. The bushes are treated with a solution of laundry soap or "Confidor", "Aktellik".
Seedling care
Young honeysuckle does not require feeding for 2-3 years if the plants are planted in prepared soil. The soil is always kept moist, without water stagnation. Once a week, the soil under the bushes is loosened to saturate it with oxygen and develop the root system.
Plants are regularly inspected for diseases and pests. If affected areas are found, seedlings are treated.
Subject to these conditions within 5 years the bushes will yield useful berries.
Conclusion
Reproduction of edible and decorative honeysuckle is not difficult. The plant is unpretentious, rarely gets sick, the survival rate of seedlings is high. Observing the timing of harvesting cuttings and creating optimal conditions for the growth of seedlings, gardeners get strong plants adapted to local natural conditions. After planting, honeysuckle grows and bears fruit in one place for up to 20 years.